Life Science Grade 12 | Study Guide | Past Papers | Revision 4
Life Science Grade 12
HUMAN REPRODUCTION
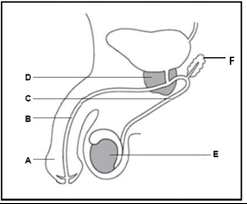
The diagram below represents a part of the male reproductive system.
Question
Give the letter and the name of the part that is used in copulation.
The correct letter is A, and this part is called the Penis.
The penis is the male reproductive organ responsible for copulation. It delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract during sexual intercourse. The structure contains erectile tissue that allows it to become firm during arousal, facilitating the transfer of sperm.
Question
Give the letter and the name of the part that produces testosterone.
The correct letter is E, and the name of the part is Testes.
The testes are responsible for producing the male sex hormone, testosterone, which plays a crucial role in male reproductive development. Testosterone is essential for sperm production, the development of secondary sexual characteristics (such as deepening of the voice and muscle growth), and maintaining overall reproductive health.
Question
Give only the letters and name of the two parts in the diagram that contribute to the formation of semen.
The first part is D, and the name of this part is Prostate. The second part is F, and the name of the part is Seminal Vesicle
The prostate gland represented by letter D and seminal vesicle; letter F both contribute fluids that form semen. The seminal vesicle produces a nutrient-rich fluid that provides energy for sperm, while the prostate gland secretes an alkaline fluid that neutralizes acidity in the female reproductive tract, enhancing sperm survival.
Question
Give the letters and name of the two parts in the diagram that provide a passage for the sperm cells.
The two parts in the diagram that provide a passage for the sperm cells are, Part C, known as the Sperm Duct or Vas Deferens and the part B, the Urethra
The sperm duct (vas deferens) indicated by letter C transports sperm from the testes to the urethra, while the urethra represented by letter B in the diagram serves as the final passage for sperm to exit the body during ejaculation. The urethra also functions in the excretion of urine, but during ejaculation, a muscular contraction prevents the mixing of sperm and urine.
The structure below represents a part of the female reproductive system.
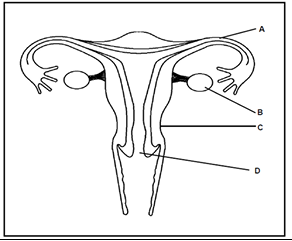
The structure below represents a part of the female reproductive system.
Question
State the function of part A.
Part A, the fallopian tube (oviduct), provides the passage for the egg to travel from the ovary to the uterus. It is also the site where fertilization by sperm usually occurs.
Question
Describe the process of oogenesis as it occurs in part B.
Oogenesis begins with diploid cells (2n) in the ovaries undergoing mitosis to form many follicles. At the onset of puberty, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the development of a follicle, causing one primary oocyte inside the follicle to enlarge and begin meiosis. During meiosis, four cells are produced, but only one survives to become the mature, haploid (n) ovum. This process occurs monthly as part of the menstrual cycle.
Question
State ways in which structure C is suited for its function during pregnancy.
Structure C, which refers to the uterus, is well-suited for its function during pregnancy due to its muscular walls. These walls enable the uterus to enlarge as the fetus develops, providing enough space to house and protect the growing fetus. Additionally, the muscular walls allow the uterus to contract during childbirth, helping to expel the baby from the womb. These characteristics are essential for both supporting the pregnancy and facilitating a safe delivery.
Question
A person undergoes a surgical operation to remove part B on both sides. Explain why this person will not menstruate.
When part B, which refers to the ovaries, is removed, the person will no longer menstruate for several interconnected reasons.
Firstly, without the ovaries, no Graafian follicles can develop. The ovaries are responsible for the formation of these follicles, which contain the eggs necessary for reproduction. Without ovaries, this key process cannot occur, and eggs are not produced.
Secondly, no oestrogen will be secreted. The ovaries are the primary source of oestrogen, a hormone that regulates the menstrual cycle. Without the ovaries, oestrogen production ceases, disrupting the hormonal balance required for menstruation.
As a result, the endometrium will not thicken. Oestrogen stimulates the thickening of the uterine lining (endometrium) in preparation for the implantation of a fertilized egg. Without oestrogen, this vital step does not take place, and the endometrium remains thin.
Lastly, without thickening, there will be no menstruation. Menstruation occurs when the endometrial lining sheds after failing to receive a fertilized egg. If the lining does not thicken in the first place, there is no need for it to shed, meaning menstruation will not occur. Thus, the removal of the ovaries leads to the cessation of menstruation.
The diagrams below show structures formed during human reproduction.
The structure below represents a part of the female reproductive system.
Question
State the function of part A.
Part A, the fallopian tube (oviduct), provides the passage for the egg to travel from the ovary to the uterus. It is also the site where fertilization by sperm usually occurs.
Question
Describe the process of oogenesis as it occurs in part B.
Oogenesis begins with diploid cells (2n) in the ovaries undergoing mitosis to form many follicles. At the onset of puberty, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the development of a follicle, causing one primary oocyte inside the follicle to enlarge and begin meiosis. During meiosis, four cells are produced, but only one survives to become the mature, haploid (n) ovum. This process occurs monthly as part of the menstrual cycle.
Question
State ways in which structure C is suited for its function during pregnancy.
Structure C, which refers to the uterus, is well-suited for its function during pregnancy due to its muscular walls. These walls enable the uterus to enlarge as the fetus develops, providing enough space to house and protect the growing fetus. Additionally, the muscular walls allow the uterus to contract during childbirth, helping to expel the baby from the womb. These characteristics are essential for both supporting the pregnancy and facilitating a safe delivery.
Question
A person undergoes a surgical operation to remove part B on both sides. Explain why this person will not menstruate.
When part B, which refers to the ovaries, is removed, the person will no longer menstruate for several interconnected reasons.
Firstly, without the ovaries, no Graafian follicles can develop. The ovaries are responsible for the formation of these follicles, which contain the eggs necessary for reproduction. Without ovaries, this key process cannot occur, and eggs are not produced.
Secondly, no oestrogen will be secreted. The ovaries are the primary source of oestrogen, a hormone that regulates the menstrual cycle. Without the ovaries, oestrogen production ceases, disrupting the hormonal balance required for menstruation.
As a result, the endometrium will not thicken. Oestrogen stimulates the thickening of the uterine lining (endometrium) in preparation for the implantation of a fertilized egg. Without oestrogen, this vital step does not take place, and the endometrium remains thin.
Lastly, without thickening, there will be no menstruation. Menstruation occurs when the endometrial lining sheds after failing to receive a fertilized egg. If the lining does not thicken in the first place, there is no need for it to shed, meaning menstruation will not occur. Thus, the removal of the ovaries leads to the cessation of menstruation.
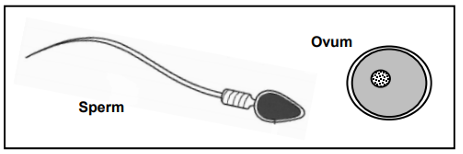
The diagram below shows a human sperm and ovum. NOTE : The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Question
Tabulate the Differences Between the Structure of an Ovum and a Sperm Cell
Table showing the Differences Between the Structure of an Ovum and a Sperm Cell
| Ovum | Sperm Cell |
|---|---|
| No tail | Contains a tail for transport |
| No mitochondria | Mid-piece contains many mitochondria |
Question
The head of the sperm contains a protein digesting enzyme. Explain the Importance of this enzyme during fertilisation.
The acrosome, located in the head of the sperm, contains digestive enzymes that are crucial for fertilization. These enzymes help to:
- Break down the outer protective layers (zona pellucida) of the ovum, allowing penetration.
- Enable the sperm cell’s haploid nucleus to enter the ovum, so fertilization can occur and a zygote can form.
Question
An active healthy sperm cell is able to swim about 4 mm per minute. If the distance from the cervix to the end of the Fallopian tube is 20 cm, how long will it take for the sperm cell to reach the ovum at the end of the Fallopian tube? Show your working.
Calculating Time for Sperm to Reach the Ovum
Given:
- Speed of sperm: 4 mm per minute – This is the rate at which the sperm moves towards the egg.
- Distance from cervix to Fallopian tube: 20 cm = 200 mm – This is the distance the sperm needs to travel to reach the ovum in the Fallopian tube.
Calculation:
Formula: Time = Distance ÷ Speed
Substituting the given values:
Time = 200 mm ÷ 4 mm/minute
We divide the total distance (200 mm) by the sperm’s speed (4 mm/minute) to determine how long it will take for the sperm to reach the ovum. This gives us a time of 50 minutes.
Answer: It will take 50 minutes for the sperm to reach the ovum at the end of the Fallopian tube.
Question
Semen has a pH of 7.5. Sperm cells have a high mortality rate in acidic conditions. How does the male body ensure that the sperm cells are not killed by acidic urine as they travel through the urethra?
During ejaculation, sperm cells pass through the urethra, which is typically an acidic environment due to the presence of urine. To protect the sperm from these harmful acidic conditions, the male body has the following mechanism in place to neutralize the acidity.
The prostate gland and Cowper’s gland (also known as the bulbourethral glands) play a key role in this protective process. These glands secrete an alkaline fluid into the urethra, which has a pH higher than the surrounding acidic environment. This alkaline fluid effectively neutralizes the acidic urine present in the urethra, creating a more favorable environment for the sperm to survive.
By neutralizing the acidity, the fluid from the prostate and Cowper’s glands ensures that sperm remain viable and able to reach the ovum for fertilization. Without this protection, the sperm would be at risk of being destroyed by the acidic conditions, which would decrease the chances of successful fertilization.
Study the human male reproductive system below and answer the questions.
Question : Identify part B
Part B is the Seminal vesicle: This gland produces and secretes seminal fluid, which nourishes and helps transport sperm.
Question: Identify Part H.
Part H is the Testes: The testes are responsible for sperm production (spermatogenesis) and the secretion of the hormone testosterone.
Question: What is the function of E?
Part E, the Urethra is responsible for transporting semen containing sperm cells during ejaculation and also serves as a passage for urine excretion from the body.
Question: Test results show that a man has a low sperm count. The doctor advises the man that when he is working on his laptop (computer),
which radiates heat, that he should not put the laptop on his lap. Why do you think this could have an influence on fertility?
Optimal sperm production occurs at a temperature 2-3°C lower than body temperature. Placing a laptop on the lap increases the temperature of the testes, which can negatively affect sperm production. This reduces sperm count and quality, leading to decreased fertility.
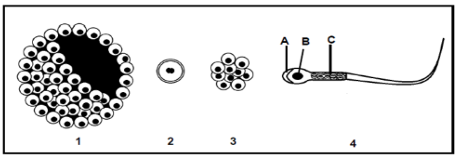
Study the diagram below of the sequence of events that takes place from the fertilization of the ovum to the development of the embryo in a part of the human female reproductive system. The arrows indicate the direction of development of one ovum after fertilisation.
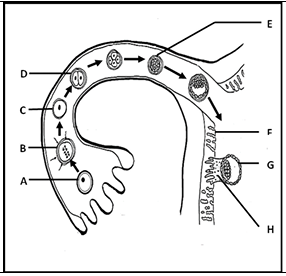
Question: Identify Structure C.
Structure C represents the zygote, which is the fertilized egg cell formed when the sperm nucleus fuses with the ovum nucleus. This marks the beginning of a new human life.
Question : Identify the stage of embryo development at E.
At E, the embryo has reached the morula stage, which is a solid ball of cells formed by rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote as it moves through the Fallopian tube.
Question : Identify, the structure that develops from a combination of parts F and H.
Parts F which is the uterus lining and H, the embryo together form the placenta. The placenta plays a crucial role in nourishing the developing fetus, supplying oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products.
Question : Name the process that takes place at B.
At B, the process of fertilization occurs, where the sperm cell successfully penetrates the ovum, leading to the formation of a diploid zygote. This initiates embryonic development.
Question
Name the process that takes place, when G attaches to part F.
When G (the developing embryo) attaches to F (the uterus lining), the process is called implantation. This is a critical step where the embryo embeds itself into the thickened endometrium, allowing it to receive nutrients and develop further.
Question
Give the chromosome number of the cells at D.
The cells at D have 46 chromosomes, as they result from mitotic divisions of the original zygote, ensuring the normal diploid number of a human cell.
Question
Give the chromosome number of cell A.
Cell A represents a haploid gamete, either a sperm or an ovum, before fertilization. Human gametes carry 23 chromosomes, which is half the diploid number, to ensure that when fertilization occurs, the zygote restores the full diploid set of 46 chromosomes. This is essential for genetic stability across generations. Therefore, before fertilization, cell A has 23 chromosomes.
Question
Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions.
The fusion of the sperm and egg outside the body
The correct answer is: External Fertilization
External fertilization occurs when sperm and egg unite outside the female’s body, usually in an aquatic environment. This method is common in fish and amphibians, where large numbers of gametes are released into the water to increase the chances of successful fertilization.
The development of the embryo inside an incubated egg that is laid
The correct answer is: Ovipary
Ovipary is a reproductive strategy in which eggs are fertilized internally or externally but develop outside the mother’s body. The embryo receives nutrients from the yolk inside the egg, and the young hatch when development is complete. This is observed in birds, reptiles, and amphibians.
The development of the embryo in the uterus and the young are born alive
The correct answer is: Vivipary
Vivipary is a mode of reproduction in which the embryo develops inside the mother’s uterus, receiving nutrients directly from her bloodstream. The young are born alive rather than hatching from eggs. This is common in most mammals, including humans.
The complete development of the embryo inside an egg in the female body
The correct answer is: Ovovivipary
Ovovivipary is a reproductive method where embryos develop inside eggs that remain within the mother’s body until they hatch. The embryo relies solely on the yolk for nourishment, and there is no direct nutrient exchange with the mother. This is seen in some sharks, snakes, and insects.
The development of the embryo in which very little energy is used and parental care is required
The correct answer is: Altricial Development
Altricial species give birth to underdeveloped young that require extensive parental care for survival. These offspring are usually born blind, hairless, and unable to move independently. Examples include birds such as pigeons and mammals like cats and humans.
The development of the embryo in which a lot of energy is used and the young are able to move directly after hatching
The correct answer is: Precocial Development
Precocial species invest more energy into embryonic development, resulting in offspring that are relatively mature and mobile at birth or hatching. These young can walk, see, and feed themselves shortly after birth. Examples include ducks, chickens, and some antelope species.
Structure that provides nutrition to the embryo in the amniotic egg
The correct answer is: Yolk Sac
The yolk sac is an essential structure inside the amniotic egg, providing nutrients to the developing embryo. It contains stored food in the form of proteins and lipids, which support growth until the embryo can survive independently. This is a key feature in the eggs of birds, reptiles, and some fish.
Fluid-filled bag around the embryo
The correct answer is: Amnion
The amnion is a protective membrane that surrounds the developing embryo and forms a fluid-filled sac. This sac provides cushioning, preventing physical damage, and helps regulate temperature and moisture levels, ensuring a stable environment for growth.
Structure in the sperm cell that contains enzymes used to penetrate the ovum
The correct answer is: Acrosome
The acrosome is a specialized structure in the head of the sperm cell that contains digestive enzymes. These enzymes help break down the outer layers of the ovum, allowing the sperm to penetrate and fertilize the egg. This process is critical for successful reproduction.
The liquid that surrounds the human embryo
The correct answer is: Amniotic Fluid
Amniotic fluid surrounds and protects the developing embryo inside the amniotic sac. It serves multiple functions, including shock absorption, temperature regulation, and allowing free movement for proper development. The fluid also contains nutrients and hormones that support fetal growth.
A hollow ball of cells into which the fertilized ovum develops
The correct answer is: Blastula/Blastocyst
The blastula (or blastocyst in mammals) is an early-stage embryo formed through repeated mitotic cell division of the zygote. It consists of a hollow sphere of cells filled with fluid, which later implants into the uterus. This stage is crucial for implantation and further differentiation into specialized tissues.
The lining of the uterus which is richly supplied with blood vessels
The correct answer is: Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus that thickens in response to hormones to prepare for potential pregnancy. If fertilization occurs, the blastocyst implants into the endometrium for nourishment. If no pregnancy occurs, this lining is shed during menstruation.
Coiled tubular structure outside the testis that stores sperm
The correct answer is: Epididymis
The epididymis is a long, coiled duct located on the back of each testis. It stores sperm and allows them to mature, gaining motility and the ability to fertilize an egg. This structure ensures that sperm are fully developed before ejaculation.
The part of the female reproductive system in which fertilization takes place
The correct answer is: Fallopian Tube/Oviduct
The fallopian tube, also called the oviduct, is where the sperm meets the ovum for fertilization. Tiny hair-like structures called cilia help move the fertilized egg towards the uterus. Blockages in the fallopian tubes can lead to infertility.
The name given to the embryo after it reaches 12 weeks
The correct answer is: Foetus
At 12 weeks, the developing embryo is called a fetus because all major organs and structures are formed. From this stage onward, the fetus grows rapidly, and its organs mature.
The hormone produced by the pituitary which controls the growth of the Graafian follicle
The correct answer is: Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
FSH is secreted by the pituitary gland and plays a crucial role in the female reproductive cycle. It stimulates the growth and maturation of the Graafian follicle in the ovary, which contains the developing ovum. In males, FSH is responsible for stimulating sperm production in the testes.
Layer within the ovary that is responsible for the formation of ova through meiosis
The correct answer is: Germinal Epithelium
The germinal epithelium is a layer of cells on the surface of the ovary that gives rise to primary oocytes through meiosis. These oocytes develop into mature eggs that can be fertilized during the reproductive cycle.
Another name for the period of pregnancy
The correct answer is: Gestation
Gestation is the period from fertilization to birth during which the embryo develops inside the mother’s body. In humans, gestation lasts approximately 40 weeks and includes various developmental stages, from a zygote to a fully formed baby.
The process by which the embryo becomes attached to the uterine wall
The correct answer is: Implantation
Implantation occurs when the blastocyst embeds itself into the thickened endometrium of the uterus. This allows the embryo to receive nutrients and oxygen from the mother’s blood supply, supporting further development.
The hormone which converts the ruptured follicle into a corpus luteum
The correct answer is: Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
LH is released by the pituitary gland and triggers ovulation. After ovulation, it stimulates the ruptured follicle to form the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to maintain the uterine lining for potential pregnancy.
Type of cell division by which sperms are produced
The correct answer is: Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing haploid sperm cells in males. This ensures that when fertilization occurs, the resulting zygote has the correct diploid chromosome number.
The 28-day reproductive cycle in females involving changes in the ovary and uterus
The correct answer is: Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a recurring process in females that prepares the body for pregnancy. It consists of four main phases: the follicular phase, ovulation, the luteal phase, and menstruation. Hormonal regulation controls the maturation of eggs and the thickening of the uterine lining.
Tearing away of the endometrium lining of the uterine wall, accompanied by the loss of blood
The correct answer is: Menstruation
Menstruation occurs when the thickened endometrium is shed due to the absence of fertilization. This process results in the discharge of blood and tissue through the vagina, marking the beginning of a new menstrual cycle.
The cell division by which the zygote becomes multicellular
The correct answer is: Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division responsible for growth and development. After fertilization, the zygote undergoes multiple rounds of mitotic division to form a multicellular embryo, leading to tissue and organ formation.
Production of ova by meiosis
The correct answer is: Oogenesis
Oogenesis is the process by which ova (egg cells) are formed in the female ovaries through meiosis. This process begins before birth, pauses until puberty, and resumes cyclically with each menstrual cycle, resulting in the maturation of a single ovum per cycle.
The hormone which starts the preparation of the lining of the uterus for attachment of the fertilized ovum
The correct answer is: Oestrogen
Oestrogen is a hormone produced primarily by the ovaries that stimulates the thickening of the endometrium. It plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle by promoting the growth of blood vessels in the uterus, preparing it for potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
Process by which an ovum is released from the ovary in humans
The correct answer is: Ovulation
Ovulation occurs when a mature ovum is released from a Graafian follicle in the ovary. This typically happens around day 14 of the menstrual cycle and is triggered by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH). The released ovum then moves into the fallopian tube, where it may be fertilized.
Gland in the brain that produces FSH and LH
The correct answer is: Pituitary/Hypophysis
The pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, secretes Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH). These hormones regulate reproductive functions by controlling ovulation in females and sperm production in males.
Combination of fetal and maternal tissue responsible for gas exchange, nutrition, and excretion
The correct answer is: Placenta
The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. It facilitates the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste between the mother and the developing fetus. It also produces hormones such as progesterone to maintain pregnancy.
Hormone that maintains pregnancy
The correct answer is: Progesterone
Progesterone is a hormone secreted by the corpus luteum and later by the placenta. It helps maintain the uterine lining, preventing contractions that could lead to miscarriage. It also supports the growth of the placenta and prepares the mammary glands for lactation
The stage when sexual maturity is reached in males and females
The correct answer is: Puberty
Puberty is the stage of human development when individuals become capable of sexual reproduction. It is marked by hormonal changes that lead to the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as breast development in females and facial hair growth in males.
Production of spermatozoa by meiosis
The correct answer is: Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which sperm cells are produced in the testes. It involves meiosis, resulting in haploid sperm cells that carry half the genetic material necessary for fertilization.
Hormone responsible for secondary sexual characteristics in males
The correct answer is: Testosterone
Testosterone is a hormone produced primarily in the testes. It is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, including deepening of the voice, increased muscle mass, and the growth of facial and body hair.
A hollow, rope-like tube that attaches the embryo to the placenta
The correct answer is: Umbilical Cord
The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta and serves as a lifeline, transporting oxygen and nutrients from the mother to the fetus while removing waste products.
The blood vessel that carries nitrogenous waste from the fetus to the placenta
The correct answer is: Umbilical Artery
The umbilical artery carries deoxygenated blood and waste products, including nitrogenous waste, from the fetus to the placenta, where they are exchanged and removed by the mother’s circulatory system.
The blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus
The correct answer is: Umbilical Vein
The umbilical vein carries oxygen-rich blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetus. This ensures proper growth and development before birth.
The structure where testosterone is produced
The correct answer is: Testes
The testes are the male reproductive organs responsible for the production of testosterone and sperm. They are located in the scrotum and contain seminiferous tubules where spermatogenesis occurs.
Sac-like structure that contains the testes
The correct answer is: Scrotum
The scrotum is a pouch of skin that holds and protects the testes. It regulates their temperature by contracting or relaxing to ensure optimal conditions for sperm production.
A gland that lubricates the end of the penis
The correct answer is: Cowper’s Gland
Cowper’s glands, also called bulbourethral glands, produce a clear mucus-like fluid that lubricates the urethra and neutralizes acidic urine before ejaculation, facilitating sperm movement.
Common tube for sperm and urine
The correct answer is: Urethra
The urethra is a tube that serves as a passageway for both semen and urine in males. It runs through the penis and allows for the expulsion of fluids from the body.
A gland that produces an alkaline medium in semen
The correct answer is: Prostate Gland
The prostate gland produces an alkaline fluid that helps neutralize the acidic environment of the vagina, enhancing sperm survival and motility.
A gland that provides nutrients for the sperm
The correct answer is: Seminal Vesicle
The seminal vesicles produce a fluid rich in fructose, which provides energy for sperm movement. This fluid also forms a major component of semen.
A tube that transfers sperm to the urethra
The correct answer is: Vas Deferens
The vas deferens is a muscular tube that transports mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra in preparation for ejaculation.
ALSO READ Business Studies Grade 12 | Study Guide | Notes | Past Exam Papers Revision 1